1 What is a data center?
A data center is a facility consisting of computer networks, storage systems and computer infrastructure for businesses and other organizations that use to organize, process, store and distribute large amounts of data. An entity generally relies heavily on applications, services and data contained within a data center, making it a focal point and an important asset in day-to-day operations.
Business data centers are increasingly incorporating security and protection services for cloud computing services, as well as internal, on-site services. As businesses gradually turn to cloud computing, the boundaries between cloud providers’ data centers and business data centers become less clear.
2 How do data centers work?
The data center allows an organization to compile its resources and infrastructure for data processing, storage, and communication, including: storage, sharing, access, and processing data across local infrastructure to support data processing and data communications; and services such as cooling, electricity, network access and uninterrupted electronic devices (UPS).
Collecting all these resources in the database enables the organization to:
protect proprietary systems and data; integrate IT and data processing staff, contractors, and vendors; apply information security controls to identity systems and data; and identify the economy of scale by integrating sensitive systems into one area.
3 Why are data centers important?
Data centers support almost all accounting, data storage, and business applications. To the extent that a modern business enterprise is run by computers, a data center is a business. Most businesses need to store data – whether it’s for their email, website, online transactions, etc. and Other factors include regional usage, infrastructure development, transportation, and anything else that can affect data centers. Currently, SDWAN technology has become popular and is becoming a trend of a new era. This technology will simplify life and be ready for use by all stakeholders. In traditional data center technology, MPLS is used to connect remote branch offices to a centralized data center, and all communication with the data center is via MPLS. For example, if someone has email or ERP, the communication is over the WAN using MPLS technology. But we are talking about the one used in 2003. Until then, by 2022, SDWAN will make life easier because everything happens using a cloud like AWS or Azure. Traditional WAN architectures have been limited to enterprises, branch offices, and data centers. As organizations adopt cloud applications in the form of SaaS and IaaS, applications will explode in WAN architectures to access globally distributed traffic. These changes have had a huge impact on IT. SaaS application performance issues can hamper employee productivity. Global network costs can increase due to inefficient use of dedicated and redundant channels. IT departments work every day to connect different users with different types of devices to different cloud environments. It helps remote branches and can get data anytime, anywhere. This is useful for SaaS applications that you use frequently, such as Office 365, and helps users get and use information when they want to access it. Data centers now use SDWAN technology. In general, solutions are expensive and not everyone can afford, so they cost a lot of money and budget. These high-tech companies are definitely moving to SDWAN to continue to develop the technology and take full advantage of its benefits.
- IT staff and data.
- computer and network infrastructure; and
- Computer security.
4 How big is a data center?
Data centers can vary greatly in size. Some locations are just a few hundred square feet, while others are over an acre. Digital Realty’s Oakland data center has 55,000 square feet of raised floor space in a 122,000square-foot building, for example, while the Digital Realty Houston data center building is 50,000 square feet in total.
5 What are the core components of Data Centers?
Data center objects are usually divided into three categories:
- Calculation
- Business data storage
- Network
The modern data center focuses on the organization’s data systems for virtual secure infrastructure, including:
- Servers.
- Under-storage systems.
- Network switches, routers, and firewalls.
- Cable
- Visible racks to organize and connect IT equipment.
Database services usually include:
- Power distribution and systems under additional power.
- Power switch.
- UPS
- Support generators.
- Air conditioning systems and data center, such as in-line cooling and computer room cooling; and
- Adequate network configuration for the network operator (Telcom).
All of this requires a virtual environment with secure access controls and enough square images to maintain a collection of infrastructure and resources.
6 How are Data Centers Managed?
Datacenter management requires managing a few different topics related to the data center, including:
- Resource management. Managing a portable data center location may include activities related to the site’s sales locations, resources, access control, and staff.
- Data center inventory or asset management. Database centers include hardware assets, as well as software licensing and output management.
- Database infrastructure management. DCIM lies at the crossroads of IT and institutional management and is often done by monitoring data center performance to improve power, equipment, and ground use.
- Technical support. The data center provides technical services to the organization, and as a result, should also provide technical support to the end-users of the business.
- Performance. Data center management includes the day-to-day operations and services provided by the data center.
There are now different categories in the data centers that will be discussed in detail. As we know there are different types of attacks that can damage the network. Perhaps, network security is an important factor considered to protect segments. We will be discussing the different categories that will protect the network from this type of attack.
6.1 The Internet Section
The Internet section will take care of the traffic of users who need an Internet connection for Limited Security and communication design. The diagram below shows the design

6.2 DMZ network
Since Internet-enabled VM servers can be moved to a different DMZ location, the firewall will split the L2 & L3 domain to create a DMZ location on the server farm to access a specific server.

6.3 Firewall component for LAN
The LAN Firewall component will take care of the entry and security of eligible ABL local users, voluntarily other clients may be subjected to wall testing if required.
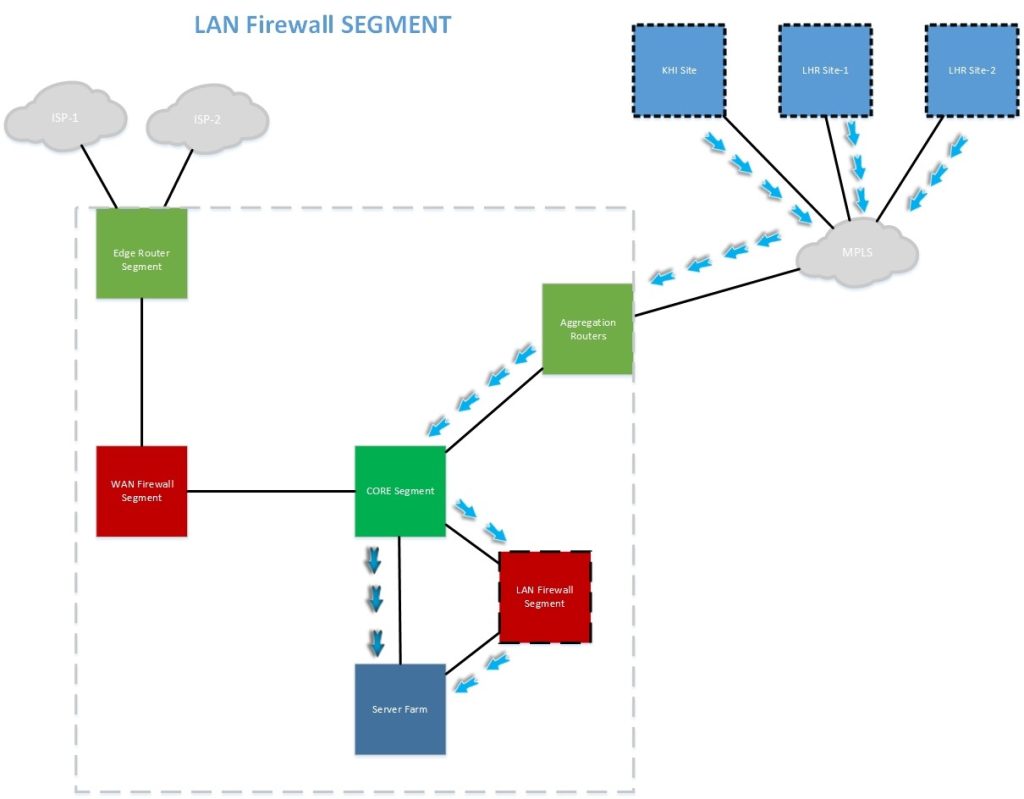
6.4 Replication Segment
Repetition will be performed between the main sites and the DR using a recurring router, which is recommended to pass recurring traffic in the firewall test.

6.5 Aggregation Network
BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) will be used with WAN segments as a sub-protocol with MPLS providers to obtain NLRI (Network Layout Information) to establish a DMVPN Tunnel between sites.

7 Data center infrastructure management and monitoring
Modern data centers make extensive use of monitoring and management software. The software, which includes DCIM tools, allows remote IT center managers to manage location and tools, measure performance, detect failures and perform multiple repair actions without actually entering the data center room.
The growth of virtualization has added another important dimension to data center infrastructure management. Virtualization now supports server deployment, networks, and storage, which allows all computer resources to be organized into pools regardless of their actual location. Administrators can then provide operational load, storage conditions and even network configuration in those common resource pools. If administrators no longer need the equipment, they can return it to the swimming pool for reuse. The entire network of actions, storage and virtualization of the server can be done with software, providing the term of the software defined in the software.
8 Energy consumption and Efficiency
Data center designs also recognize the importance of energy efficiency. A simple data center may require only a few kilowatts of power, but business data centers may require more than 100 megawatts. Today, the green data center, designed with minimal impact on the environment through the use of low-emission building materials, catalytic converters and other energy technologies, is growing in popularity.
Data centers can also maximize efficiency with their visual architecture using a method known as the hot spot and cold architecture. Servers are lined up in alternating rows where the cooling inlet is facing one direction and hot air outlets in the other. The result is a rotation of hot and cold corridors, exhauses create a hot spot and inputs create a cold environment. The exhauss points to the air conditioner. Utilities are usually placed between server cabinets in the queue or hallway and distribute cold air back to the cold area. This suspension of the air conditioning device is known as line cooling.
Organizations often measure the energy efficiency of a data center using a metrics called power consumption (PUE), which represents the total amount of energy that enters a database divided by the energy used by IT equipment. However, the subsequent increase in virtualization has allowed for more productive use of IT equipment, resulting in higher efficiency, lower power consumption and reduced energy costs. Metrics like PUE are no longer the essence of energy efficiency goals, but organizations can still measure PUE and use comprehensive energy analysis and analysis to better understand and manage energy efficiency.
9 Data center Tiers
Tier IV data center provides less operating systems and higher security.
Categories can be categorized by available resources, data center capabilities, or overtime guarantees. Uptime Institute defines the data center categories as follows:
Category I. These are the most basic type of data center, and include the UPS. Tier I data centers do not provide idle systems but must guarantee at least 99.671% downtime.
Phase II. These data centers include system, power, and cooling and guarantee a minimum downtime of 99.741%.
Phase III. These data centers offer partial error tolerance, 72 hours of opt-out protection, full downtime, and a 99.982% uptime guarantee.
Category IV. These data centers guarantee 99.995% of downtime – or no more than 26.3 minutes of downtime per year – as well as full error tolerance, system downtime, and 96 hours of downtime.
10 Datacenter Architecture and Design
While almost any suitable space can function as a data center with imagination, deliberate design and use of a data center requires careful consideration. Apart from the basic cost and tax issues, sites are selected based on conditional factors, such as geographical location, seismic stability and weather, access to roads and airports, access to power and communications, and the prevailing political climate.
Once the site is secure, the architecture of the data center can be designed with due regard to the mechanical and electrical infrastructure, as well as the design and layout of IT assets. All of these problems are driven by the acquisition and efficiency of the objectives of the required data center category.
11 Data Center Security and Safety
Database projects should also implement sound security and protection procedures. For example, security often comes from door systems and access corridors, which must be aligned with the movement of large, unmanaged IT assets, as well as allowing employees to access and repair infrastructure.
Fire extinguishers are another important safety feature, and the widespread use of sensitive, electronic, and electronic devices prevents routine spraying. Instead, data centers often use environmentally friendly fire extinguishing systems, which effectively starve the oxygen fire while minimizing co-operative damage. Because the data center is also a core business asset, comprehensive security measures and access controls are required.
These may include:
- badge access.
- Biometric access control; and
- video viewing.
When used properly, these safety measures can help detect and prevent the inefficiency of employees, contractors, and intermediaries.
12 What is data center consolidation?
There is no need for a single data center, and modern businesses can use two or more database installs in multiple locations to enhance the capabilities and better performance of applications, which reduces delays by placing workloads closer to users.
In contrast, a business with multiple data centers may choose to merge data centers, reducing the number of sites to reduce IT operating costs. Consolidation usually occurs during consolidation and acquisition where the majority of the business does not need the underlying business data centers.
13 Evolution of data centers
The origins of early data centers can be traced back to the 1940s with the advent of early computer programs such as Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer (ENIAC). The original equipment was intricate and functional and had many cables that connected all the necessary parts. They were also used by the military – meaning special computer rooms with racks, cable trays, cooling equipment, and access restrictions were required to both install all equipment and implement appropriate safety measures.
However, it was not until the 1990s, when IT operations began to experience difficulties and affordable communication technologies became available, that the term data center came into use. It was possible to store all the required company servers in the company’s internal room. These specialized computer rooms are called data centers within organizations, and the term gained momentum.
During the dot-com boom in the late 1990’s, the need for high speed internet and the ever-present internet presence of companies required larger resources to put in place the maximum amount of communication equipment needed. It was during this time that data centers became popular and began to resemble those described above.
In the history of computers, as computers become smaller and networks become larger, the data center has evolved and evolved to embrace the necessary technologies of the day.
14 Types Of Data Centers
Data centers vary in size, from the small server room to clusters, but they all share one thing in common: they are an important business asset where companies often invest and use the latest developments in data center connectivity, calculation. , and storage technology.
The modern data center has evolved from an institution that contains existing infrastructure to those that integrate local systems with cloud infrastructure where networks, applications, and workloads are actively deployed in many private and public clouds.
Business data centers are usually built and used by a single organization for their internal purposes. These are common among tech giants.
Colocation data centers serve as a type of rental facility where data center facilities and facilities are made available to potential tenants.
Managed service data centers offer features such as data storage, computing, and other services such as an external, customer-oriented service.
Cloud data centers are distributed and sometimes provided to customers with the help of a third-party service provider.
14.1 Evolution of the Data Center to the Cloud
The fact that virtual cloud DC can be downloaded or downloaded with just a few clicks is a major reason for switching to cloud. In modern data centers, software-defined networking (SDN) controls the flow of traffic through software. Infrastructure offerings such as IaaS, hosted on private and public clouds, cover all systems where needed. When new applications are required, Platform as a Service (PaaS) and container technology are readily available.
Many companies are moving to the cloud, but it is not something that others are willing to take. In 2019, it was reported that businesses were paying more per year for cloud infrastructure services than real-time hardware. However, a survey conducted by the Uptime Institute found that 58% of organizations claim that the lack of visibility, transparency, and accountability of public cloud services keeps a heavy burden on corporate data centers.
14.2 Principles of Data Center Infrastructure Design
Your data center is the most important resource within your organization. As you know, it provides access to all of your data storage, management, and distribution systems, applications, and communications. When employees and customers do not have access to servers, storage systems, and network devices located in the data center, your entire organization may shut down. Millions of dollars could be lost in a matter of minutes in businesses such as banks, airlines, shipping companies, and online brokerages. Faced with these results, IT managers today need to upgrade their data centers, such as their Cisco Data Center or others, especially network infrastructure. Considering that 70% of network failures can be caused by surface layer problems, especially cable errors, it is very important to take a closer look at infrastructure construction.
A data center is the home of computer power, storage, and applications needed to support a business environment. The data center infrastructure is located in the center of the IT building, where all the content is taken or passed. Properly planning the data center infrastructure design is important, and efficiency, durability, and scalability should be carefully considered.
Another important aspect of a data center design is flexibility in faster deployment and support for new services. Designing a flexible architecture with the ability to support new applications in a short period can generate a significant competitive advantage. Such a design requires strict initial planning and thoughtful consideration in the downtown areas, uplink access bandwidth, actual server capacity, and over-registration, to name a few.
The design of the data center network is based on a proven layout, which has been tested and developed over the past few years in some of the largest data centers in the world. The horizontal approach is the basis of a data center design that seeks to improve scale, performance, flexibility, durability, and care.
The layers of data center design are the contexts that are contextual, integral, and accessible. These layers are summarized as follows:
Key Layer – Provides a flexible backplane for a high-speed packet for all flow in and out of the data center. The main layer provides connectivity to multiple integration modules and provides a flexible layer of 3 layers with no single point of failure. The main layer uses an internal route protocol, such as OSPF or ISIS, and the load balances traffic between the campus spine and the integration layers.
Integration layer modules – Provide key functions, such as integration of the service module, Layout 2 domain definitions, extended tree processing, and automatic gate duplication. Multi-category server traffic flows through the integration layer and can use services, such as firewall and server load balancing, to configure and protect applications.
Access layer – Where servers attach to a network. Server components include 1RU servers, blade servers with integral switch, blade servers with transit cable, integrated servers, and mainframe with OSA adapters. The network access network infrastructure consists of modular switches, 1 or 2RU rooted configuration, and key blade server switches. The switch provides both Layer 2 and Layer 3 headers, completing the streaming domain for various servers or management requirements.
Principle 1: Space Saving
Environmentally friendly homes are expensive. Datacenter racks and equipment can take up a large number of homes for sale, and the future need for more network connectivity, bandwidth, and storage may require more space. With less space as low as high concerns among IT executives today, maximizing space resources is a very important aspect of data center design. Business conditions are constantly evolving, and as a result, the needs of the data center are constantly changing. Providing more empty floor space when designing your data center allows for flexibility to redistribute space for a specific task, and add new racks and equipment as needed.
Principle 2: Honesty
Uninterrupted service and continuous access are essential to the day-to-day running and production of your business. Since downtime translates directly into revenue loss, data centers should be built on carelessness, insecurity, and availability. Datacenter reliability is also defined by infrastructure performance. As information is sent back and forth within your facility and abroad, large data sources are transferred to and from the machine environments at very high data rates. The infrastructure must continuously support data flow without errors that cause redundancy and delays. As networks grow and demand bandwidth requirements grow, the data center infrastructure must be able to maintain continuous reliability and performance.
Principle 3: Management
Management is the key to improving your data center. Infrastructure must be built as a reliable and flexible resource to meet disaster recovery, development, and disaster recovery. Strategic management, integrated cable management that keeps cable and connections maintained and organized in a way, easy to find and access, and easy to redesign.
Cable rail routes should be clearly defined and easy to follow while allowing for easy installation, separation, access, reduced congestion, and growth area. This is especially important for data centers with a large volume of cables. Cables operated in this way improve network reliability by reducing the risk of cable damage, curved radius breakage, and the time required for identification, tracking, and rearrangement of cables.
The use of a central patch in the connection mode provides a sensible and easy-to-manage infrastructure where all network features have a permanent supply cable that has been disconnected, and can no longer be handled. The benefits of using a centralized lease on your data center include:
Reduce operating costs by significantly reducing the time it takes to repair, upgrade, and maintain.
Improved reliability by making changes in the amendment area can facilitate the connection of sensitive assets.
Reduced downtime risk by being able to split network components to resolve a problem and resume circuits in a disaster recovery environment.
15 THE FUTURE OF DATA CENTRES – TRENDS AND INDUSTRY OVERVIEW
A global epidemic has brought a new set of challenges to the world. It has forced companies to work remotely and to teach far-flung schools – and in many cases, to accelerate their creative process. As a result, the need for faster access to information has become a major challenge for data centers. According to Statista.com, the total amount of data created, copied, copied, and used worldwide is estimated to reach 79 zettabytes by 2021 generally, most of you are driven by IoT growth, it is not an easy task. The epidemic has highlighted the important role of data centers not only in ensuring that IT companies operate but also in the daily lives of ordinary users.
15.1 Data Centres: Industry overview
The data center services market was estimated at $ 48.9 billion by 2020. It is estimated that by 2026 this figure will rise to $ 105.6 billion.
- Next General in the form of remote work,
- Digital integration of existing processes,
- A growing industrial sector using digital technology,
- Increasing number of SMEs using digital technology,
- Increased use of Over-the-Top (OTT) services, a new way to deliver film and television directly online, without the need for regular cable or satellite streaming,
- Development of data production and data-hungry technologies, such as IoT or Machine Learning (ML).
We see significant growth in technologies that require data centers – for example, the growing demand for cloud services, whose providers prefer external data centers. This is a trend as internal data centers require enormous investment, both in their design and subsequent maintenance.
16 Datacenter Trends
16.1 Automation
One of the consequences of the global epidemic was the way work changed online. Although, in line with this, the number of employees allowed on site is significantly reduced in many countries. One of the ways in which future data centers will deal with such problems is to do automated work fully or partially, by optimizing AI and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) solutions.
16.2 Edge computing
Edge computing will play a major role in the development of future data centers. As more and more people find smart solutions, not only in companies but also in their own homes, the demand for edge computing will continue to grow, as will the demand for computer peripherals. This will change data centers as computer power transfers will have a direct impact on the type of data center we will see in the future. According to Statista.com, the value of a smart home market globally will rise to $ 53.45 billion by 2022.
It is also worth considering the relationship between edge computing and the 5g network as an alternative to older data centers, which will allow for faster development of AI or IoT-related applications.
Edge computing allows data to be processed closer to the source, reducing latency. This may lead to the development of mobile data centers, which can be easily accessible, for example, near major sporting events, concerts, etc. This solution can also eliminate network problems.
16.3 Sustainability
As businesses become more aware of climate change and are urged to take immediate action, data centers also need to incorporate sustainability into their strategies.
According to the Journal of Science, data centers accounted for 1% of total global energy use. However, the activity of data centers between 2010 and 2020 increased by 6 times, while the rate of power consumption did not increase in proportion to these numbers. This reflects advances in data center technology in the form of new CPU technologies and energy-saving storage solutions such as Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe).
However, future data centers are set to be more environmentally friendly. Demand for data storage will certainly not decrease, but data centers will grow and improve their use of data compression, duplication, and other ways to improve efficiency. An additional feature is that the cooling of modern data centers is done by liquids or so-called impenetrable systems. Air cooling, which has been used to date to maintain good server performance, consumes a large number of resources. Liquid cooling, on the other hand, allows for a rapid decrease in temperature and energy consumption and is often set as a closed natural cycle. Slightly cooler systems with the latest technology in terms of components that use less energy and tolerate higher temperatures will become more prominent in the future.
Future data centers are also being designed and optimized for optimal performance. A good example of this is Google, Facebook, and Amazon, who have purchased land in Sweden for the construction of data centers, as in a cool environment few resources are needed to cool the servers. Microsoft is taking a very unusual, but very promising route with Project Natick, exploring options for submitting underwater datacenters. Located at the bottom of the ocean, covered with depleted oxygen, moisture, and nodules, data centers can appear to thrive. At least the Naticks underwater data center with 864 servers and 27.6 decibate disk (approximately 27.6 million gigabytes) showed a failure rate of 1/8 of the global control group, according to Microsoft. And with natural sea water acting as a coolant, it will be a natural victory.
17 Data Center Design & Construction
Data centers are important to the web. They handle online storage tools. Includes server racks, multiple cables, and a list of other resources. Tools store information you find on websites and other online platforms. They have to stay and work well at all times, otherwise these stadiums will not be accessible. Data centers are designed to keep servers running and operating at the appropriate levels. The data center must meet certain requirements in order to be considered efficient and reliable. So, what really goes into data building and construction?
Here is a summary of five key elements that every data center needs to address.
- Power
Data centers use more power than developed countries. Globally, data centers use more than 200 terawatts per year. They need power to keep servers and other important things in place – power outages lead to costly downtime and resource damage.
Data centers derive most of their power from the power grid. Many switch to green energy practices such as harvesting solar energy to supplement the supply from the grid – and reduce the impact on the environment. It is also important that every data center should have a power supply system (UPS) to avoid power outages.
Note: The energy demand for power stations continues to grow as servers and other resources become more complex. Thus, data centers should increase their capacity to provide electricity with a special focus on green energy.
- Cooling
Servers and other equipment in data centers generate a lot of heat. The heat builds up in the facility and has to be expelled to protect the equipment–the heat damages servers and other equipment and can even start fires.
Every data center should have efficient cooling solutions. There is a variety of cooling solutions, and every solution comes with varying requirements.
- Security
Cyber-security has been a trending topic in the past. However, even the most advanced of online security measures have no effect other than the security of the web-based data centers.
Violation of the data center will put sensitive data at risk. Thus, every data center should be protected from physical threats. Recommended safety measures include:
- Circuit fence using moving sensors and cameras
- Biometric security systems
- Guard patrols in the yard.
Only authorized employees should have access to the data center, and the number of authorized employees should be reduced to a minimum.
- Scalability
The web is getting bigger by the day, so the demand for data centers is growing exponentially. Existing data centers will soon need to host more Internet forums, which means taking up more servers and other resources. Therefore, the design and construction of a data center should account for flexibility and flexibility – all data centers should be ready to accept improvements whenever needed.
- Location
The data center is also looking for a suitable outdoor location, so the location should be close to perfect. There are several factors to consider when choosing a suitable location. Check out the following features in your list when checking for locations that may be suitable:
- There is no risk of landscaping
- Being close to a reliable energy source
- Being close to a local customer
- Predictable weather patterns
Other factors include regional usage, infrastructure development, transportation, and anything else that can affect data centers.
Currently, SDWAN technology is becoming popular and becoming a trend of a new era. This technology makes life easier and is ready for use by all stakeholders. In traditional data center technology, MPLS is used to connect remote branch offices to a centralized data center, and all communications are via MPLS to the data center. For example, if someone has email or ERP, the communication is done over a global network using MPLS technology. But we are talking about the one used in 2003. For now, in 2022, SDWAN makes life easier as everything will happen using a cloud like AWS or Azure. Traditional WAN architectures have been limited to enterprises, branch offices, and data centers. As soon as organizations adopt cloud-based applications in the form of SaaS and IaaS, WAN architectures will see an explosion of globally distributed traffic access applications.
These changes have a huge impact on IT. SaaS application performance issues can reduce employee productivity. Global network costs can increase due to inefficient use of dedicated and redundant channels. IT departments struggle every day to connect different types of users with different types of devices to different cloud environments. This helps remote branches and can receive data anytime, anywhere. This will be helpful for SaaS applications like Office 365 that they use frequently, and will help users get and use information whenever they want to access it. Data centers are now using SDWAN technology. In general, solutions are expensive and not everyone can afford, so it costs a lot of money and budget. These high-tech companies are definitely moving to SDWAN to keep evolving the technology and taking full advantage of it

 To all knowledge
To all knowledge